Influence of the measurement methods on the experiment results
On the determination and analysis research method for the human tooth enamel and dentine elements, with the development of science and technology, the detection methods gradually increase, and there are dozens of methods now[11], including atomic emission spectrometry, atomic absorption spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, secondary ion mass spectrometry, neutron activation analysis, electron probe analysis, scanning proton microprobe, laser microprobe method, proton laser X-ray emission analysis, ion selective electrode and so on.
Spectrophotometry is one of them and employed in this study, considering that the data show the higher content of calcium and phosphorus elements in the human dental enamel and dentine. Spectrophotometric method with simple operation and less specimen demand and high precision is very suitable for measuring the macro elements in human teeth. In addition, the titration method also has higher measurement accuracy for macro elements with the advantages of less specimen demand and simple operation. Therefore, the above two test methods are adopted in this experiment to determine calcium and phosphorus content.
Influence of different age and different kinds of teeth on the experiment results
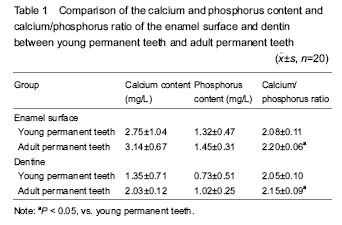
One key step in this experiment is to select the specimens of adult and young permanent teeth, and the distinction between adult and young permanent teeth in oral medicine is whether the enamel mineralization is mature or not[12]. Through long-time mineralization, the calcium and phosphorus elements are relatively stable for the adult permanent teeth, and with prolonged time, there are no obvious changes in the calcium and phosphorus elements. It is critical for selecting the age of adult permanent teeth. The adult permanent teeth in vitro from adults aged 25-50 years old are taken as the range of options in this experiment, and thus, it can guarantee the individual stability of calcium and phosphorus, which has a great significance on the experimental precision. For the age of young permanent teeth, it is more difficult for collection and sampling. Young permanent teeth just erupt in the oral cavity. Although the basic form of the young permanent teeth is basically the same to the same name teeth in the mouth for many years, it is not fully mature on the morphology and structure. Therefore it is also called the immature permanent teeth or the new eruption of permanent teeth. Considering their special characteristics, the young permanent teeth that collected in this experiment were the teeth for orthodontics with 12-14 years old. In this period, the permanent teeth just erupt and its mineralization degree is inferior to that of adult permanent teeth; therefore, there is significance to measure young permanent teeth. In terms of the kinds of teeth, the bicuspids that extracted for orthodontic need were adopted in the experiment, and premolar has big advantage relative to the anterior teeth and molar: for example, easy to collect with small attrition. On selecting the dental surface, the buccal surface of teeth was selected in this study, and its advantage lies in large area of buccal surface that is convenient to take teeth section with small abrasion than that of occlusal surface.
Mineralized degree impacts the effect of acid etching[13]
Enamel mineralization[14]: The main ingredient of enamel is the inorganic matter-hydroxyapatite, and its chemical formula is Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6. The enamel with complete hardening only contains 4% of organic matter, and inorganic matter can occupy as high as 96%. From chemical formula, we can see that the main element of hydroxyapatite is calcium and phosphorus. The formation of the dental enamel: in forming process, the enamel and dentin rhythmically, regularly and crosswise develop. The odontoblasts first form one layer of dentin and retreat to the center of dental pulp, and then the emailloblasts secrete one layer of enamel and retreat outward. This process continues so alternately with layer-by-layer deposition, until reaching the appropriate thickness of dental crown. Its specific process is as follows:
Secretory period: Inner enamel epithelium-change in function and polarity-former ameloblast, secretory period: after the forming dentin, the dentin (induction)-former ameloblast (differentiation)-ameloblast (secretion)-matrix. The cells begin to leave enamel-dentinal junction and protrude TOM’s process on reaching enamel-dentinal junction, and to secrete enamel until reaching the former thickness of enamel in dental crown. Mature period (namely the mineralization period: When the enamel matrix is secreted enough in the thickness, it begins to be mineralized. The modes for enamel mineralization mainly are: (1) mineral salt deposit to matrix. (2) The protein and water in matrix is absorbed continuously and alternately repeatedly, thus reaching the enamel mineralization of 96%. Enamel mineralization can be divided into four periods: (1) 30% mineralization can be gotten immediately after the forming enamel matrix, but the maximal mineralized degree lies in enamel-dentinal junction. (2) The mineralization begins from the outward layer of enamel--deep diffusion. (3) The mineralization begins from the inner layer of enamel--surface diffusion. (4) The enamel at outward layer gets quick mineralization and becomes the highest mineralized position in the enamel.
Enamel mineralization is controlled by emailloblasts, the striated border and smooth border of emailloblast appear alternately. For the striated border structure, the inorganic ion is exuded; for the smooth border structure, the protein and water is absorbed. This process runs throughout the process of enamel matrix secretion.
The specific steps of dentin formation[15]: In late bell stage, the inner enamel epitheliums of enamel organ complete differentiation and maturity, and induce dental papilla. The human dental papilla cells that contact the basement membrane of the inner enamel epithelium differentiate into odontoblasts that are in a shape of high columnar. Differentiated odontoblasts begin to form the organic matrix of dentin. Odontoblasts synthesize the collagen type I and secret it into the matrix of dental papilla. The collagen fiber that is first secreted out of cells is larger, which is distributed in the matrix below the basement membrane and perpendicular to basement membrane. These bulky fibers and the matrix form the earliest dentin matrix together, namely the mantle dentin. As odontoblasts increase in volume, the extracellular space disappears, and the cells protrude their stubby process to one side of basement membrane; at the same time, the cell body moves to the center of dental pulp and leaves behind the cytoplasmic processes that embedded in the matrix, forming the odontoblastic process. Occasionally, some process can pass through the basement membrane and form the enamel spindle. While forming the odontoblastic process, some vesicles that enveloped in membrane appear, which are called matrix vesicle and are secreted among larger collagen fibers. The apatite in the extracellular vesicles exists in the form of single crystal. Then, the crystal grows up with vesicle rupture, and the crystal in the vesicle is scattered in protuberant surrounding and dentin matrix in clusters. The crystal continues to grow up with mutual fusion, and finally, form the mineralized dentin.
As the early stage of adult permanent teeth, the content of enamel fiber in young permanent teeth is relatively less than that of adult permanent teeth[16], its organic matter is more than that of adult permanent teeth[17], but its spatial structure is not perfect as that of adult permanent teeth. Therefore, the structure of young permanent teeth is not compact as adult permanent teeth with more porous structure, which needs time to be perfected. The mineralized degree of young permanent teeth needs to be continuously strengthened as time goes on; thus, the content of organic matter is reduced continuously compared with that of inorganic matter, with more less acid proof organic matter. Ultimately, the content of inorganic matter is same to that of adult permanent teeth, which is beneficial to the post-acid-etching effects, and further affects the bonding effect[18]. Therefore, lower mineralization in young permanent teeth than adult permanent teeth may influence the effect of acid etching and the bonding technology[18]. In view of above analysis and discussion, the acid etching time for young permanent teeth at clinical treatment can be extended appropriately, in order to achieve the same acid etching effect as adult permanent teeth[19].